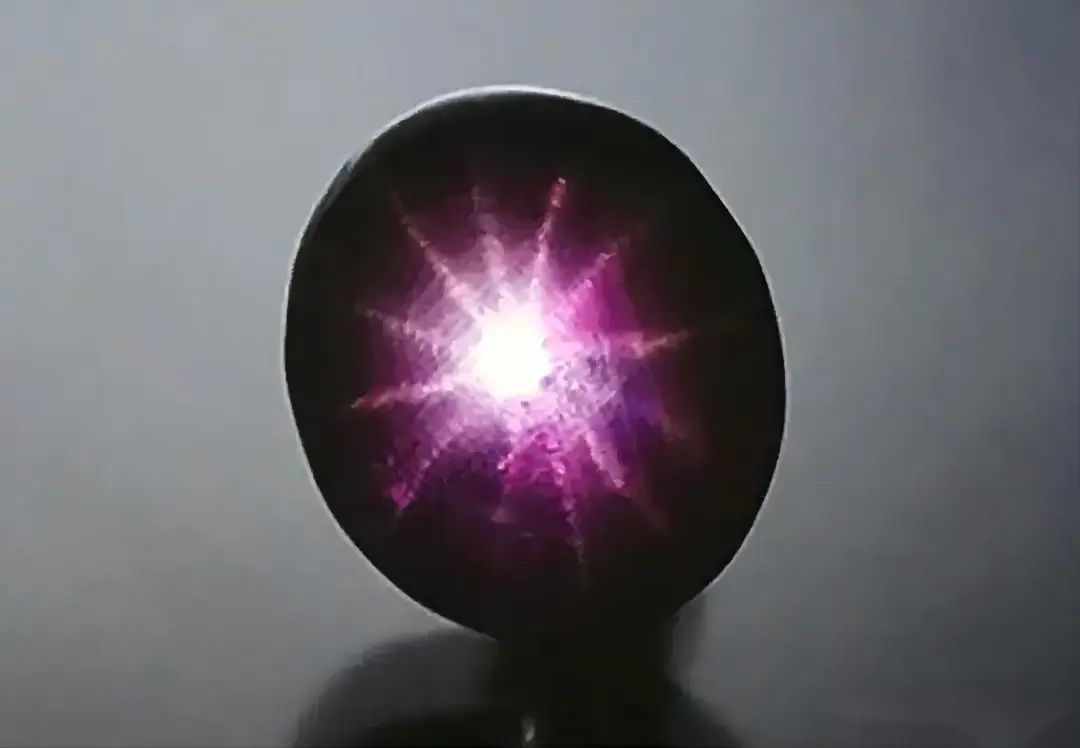
1. Starlight effect
Curved cabochon gems during irradiation with a point light source show contrasting optical phenomena with 4, 6, or 12 shots of star-like rays. His example, called the Starlight effect, is like the starlight of the night sky. Ruby and sapphire are formed by including the silky rutile inside, which is placed in parallel.

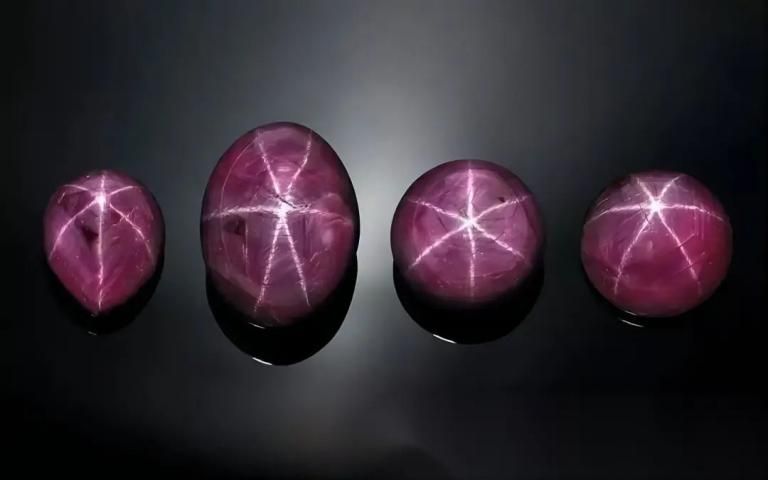
Asteristic gems: Ruby jewels, Sapphire jewels, spinels, garnets, diopside, Tourmatine, etc.

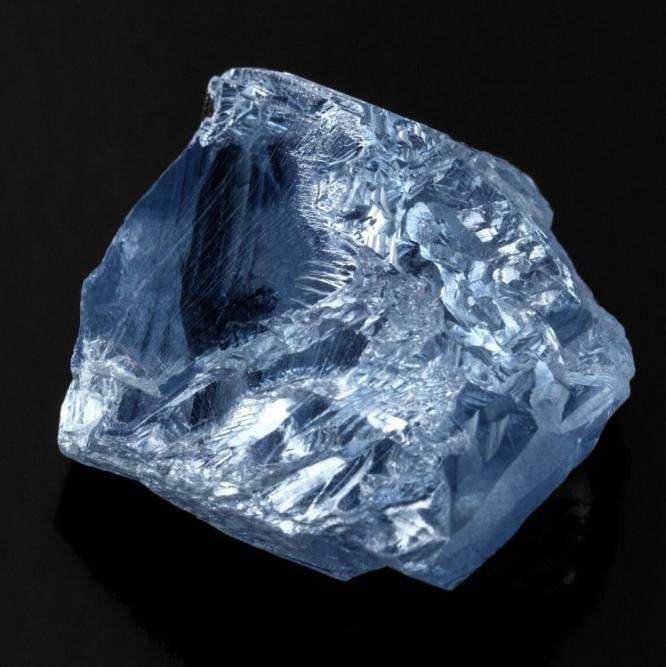
This blue diamond, weighing 39.35 ct before being cut, was discovered in the "C-Cut" area of the Cullinan mine in South Africa in April 2021. This blue diamond was purchased by De Beers Group and US diamond cutter Diacore. gross for $40.18 million in July 2021 and was officially named the hijack.



* Basically, the formation principle of the Gemster effect is the same as the cat's eye effect. This is caused by the refraction and reflection of visible light from gem inclusions or directional structures. The difference is that there is only one cluster inside the gem and it shows a "cat's eye effect" after one of the horns is polished. The packages are sorted at different angles and polished at specific corners, but with a "star effect".
You can understand it as: the starlight effect is an upgraded version of the cat's eye effect
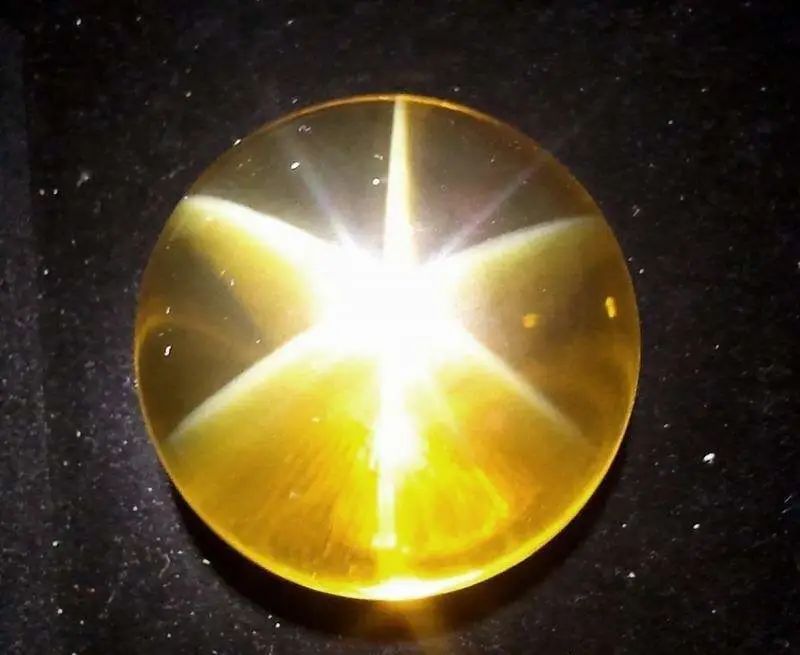

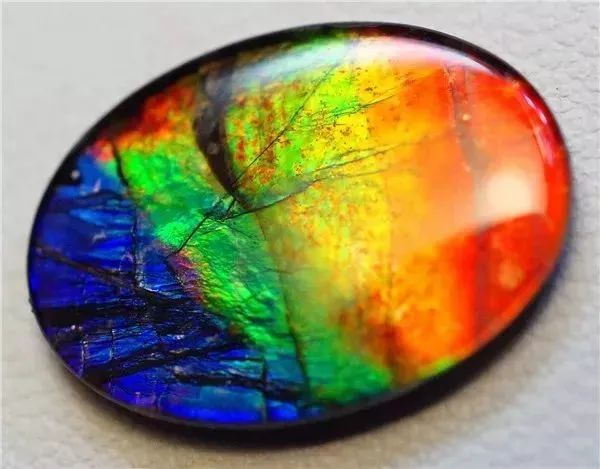
2. Color changing effect.
when illuminated The same gem shows silky hues or flecks of different colors. As you rotate the gems the light source will change the rainbow color point. This is the diffraction effect of light.
Common gems that can produce a color change effect are opals and jars.



Post time: May-13-2022